Improving Artificial Teachers by Considering How People Learn and Forget
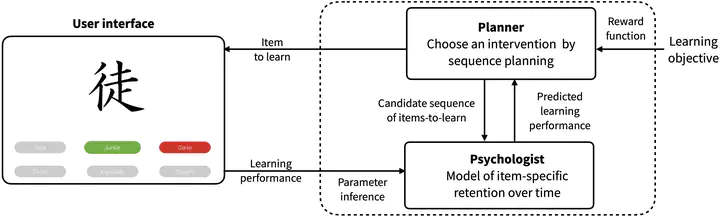
See the external project page.
The paper presents a novel model-based method for intelligent tutoring, with particular emphasis on the problem of selecting teaching interventions in interaction with humans. Whereas previous work has focused on either personalization of teaching or optimization of teaching intervention sequences, the proposed individualized model-based planning approach represents convergence of these two lines of research. Model-based planning picks the best interventions via interactive learning of a user memory model’s parameters. The approach is novel in its use of a cognitive model that can account for several key individual- and material-specific characteristics related to recall/forgetting, along with a planning technique that considers users’ practice schedules. Taking a rule-based approach as a baseline, the authors evaluated the method’s benefits in a controlled study of artificial teaching in second-language vocabulary learning (N = 53).
Venue
- CORE ranking: A
- Scholar ranking: #13 HCI, 40 h5-index
- Acceptance rate (2018): 23%
Acknowledgments
We thank all study participants for their time, and our colleagues and the reviewers for their helpful comments. This work was funded by Aalto University’s Department of Communications and Networking (Comnet), the Finnish Center for Artificial Intelligence (FCAI), the Foundation for Aalto University Science and Technology, and the Academy of Finland (projects 328813, “Human Automata,” and 318559, “BAD”). We also acknowledge the computation resources provided by the university’s Science-IT project.