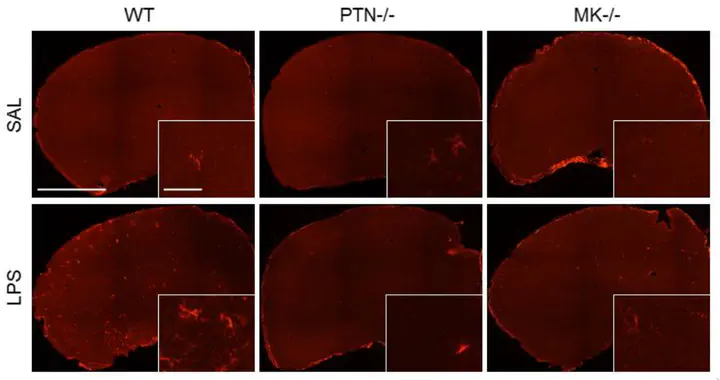
- Pleiotrophin (PTN) and Midkine (MK) are two growth factors that modulate neuroinflammation. They are overexpressed with certain diseases.
- Animal models expressing or not these molecules are exposed to different concentrations of a pro-inflammatory substance (LPS).
- The effect is assessed by looking at whether some cell types are activated (astrocytes and microglial cells).
- In conclusion, the regulation of astroglial responses to LPS administration is highly dependent on the levels of expression of PTN and MK.
Abstract
Pleiotrophin (PTN) and Midkine (MK) are two growth factors that modulate neuroinflammation. PTN overexpression in the brain prevents LPS-induced astrocytosis in mice but potentiates microglial activation. The modest astrocytic response caused by a low dose of LPS (0.5 mg/kg) is blocked in the striatum of MK-/- mice whereas microglial response is unaffected. We have now tested the effects of an intermediate dose of LPS (7.5 mg/kg) in glial response in PTN-/- and MK-/- mice. We found that LPS-induced astrocytosis is prevented in prefrontal cortex and striatum of both PTN-/- and MK-/- mice. Some of the morphological changes of microglia induced by LPS tended to increase in both genotypes, particularly in PTN-/- mice. Since we previously showed that PTN potentiates LPS-induced activation of BV2 microglial cells, we tested the activation of FYN kinase, a substrate of the PTN receptor RPTPβ/ζ, and the subsequent ERK1/2 phosphorylation on LPS and PTN-treated BV2 cells. LPS effects on BV2 cells were not affected by the addition of PTN, suggesting that PTN does not recruit the FYN-MAP kinase signaling pathway in order to modulate LPS effects on microglial cells. Taking together, evidences demonstrate that regulation of astroglial responses to LPS administration are highly dependent on the levels of expression of PTN and MK. Further studies are needed to clarify the possible roles of endogenous expression of PTN and MK in LPS-induced microglial responses.
Venue
- Impact factor: 2.376 Q3
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by grants SAF2014-56671-R from Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad of Spain, PNSD001I2015 from National Plan on Drug abuse, Ministerio de Sanidad, Servicios Sociales e Igualdad of Spain. M V-R and R F-C were supported by fellowships from Fundación Universitaria San Pablo CEU.