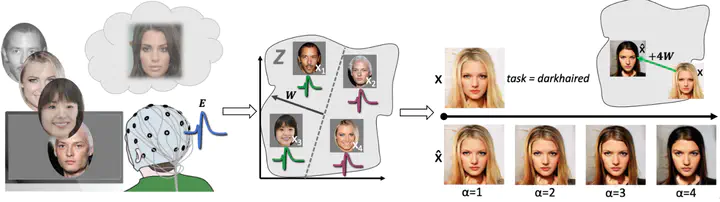
- Current image semantic editing approaches rely on manual annotations or use unsupervised techniques that require a human to assess semantic relevance.
- We propose a novel paradigm in which we measure implicit responses direcly from the brain (EEG) to detect feature saliency and use them for image editing.
- We evaluate the approach by independent evaluators in an offline study showing significant performance compared with a random baseline, and comparable performance to manual feedback.
Abstract
Despite recent advances in deep neural models for semantic image editing, present approaches are dependent on explicit human input. Previous work assumes the availability of manually curated datasets for supervised learning, while for unsupervised approaches the human inspection of discovered components is required to identify those which modify worthwhile semantic features. Here, we present a novel alternative: the utilization of brain responses as a supervision signal for learning semantic feature representations. Participants (N=30) in a neurophysiological experiment were shown artificially generated faces and instructed to look for a particular semantic feature, such as “old” or “smiling”, while their brain responses were recorded via electroencephalography (EEG). Using supervision signals inferred from these responses, semantic features within the latent space of a generative adversarial network (GAN) were learned and then used to edit semantic features of new images. We show that implicit brain supervision achieves comparable semantic image editing performance to explicit manual labeling. This work demonstrates the feasibility of utilizing implicit human reactions recorded via brain-computer interfaces for semantic image editing and interpretation.
Video
Venue
- CORE ranking: A* flagship
- Scholar ranking: #4 General, #1 Eng&CS, 389 h5-index
- Acceptance rate: 25.33%
Acknowledgments
This research was partially funded by the Academy of Finland. Computing resources were provided by the Finnish Grid and Cloud Infrastructure (urn:nbn:fi:research-infras-2016072533). We thank Michiel Spape for his contributions to the neurophysiological experimentation and advice.